OTOPLASTY, SURGERY FOR PROMINENT EARS
Otoplasty is a surgical procedure that can be performed as early as the age of 6, including adults. The incision (and so the scar) is made behind the ear.
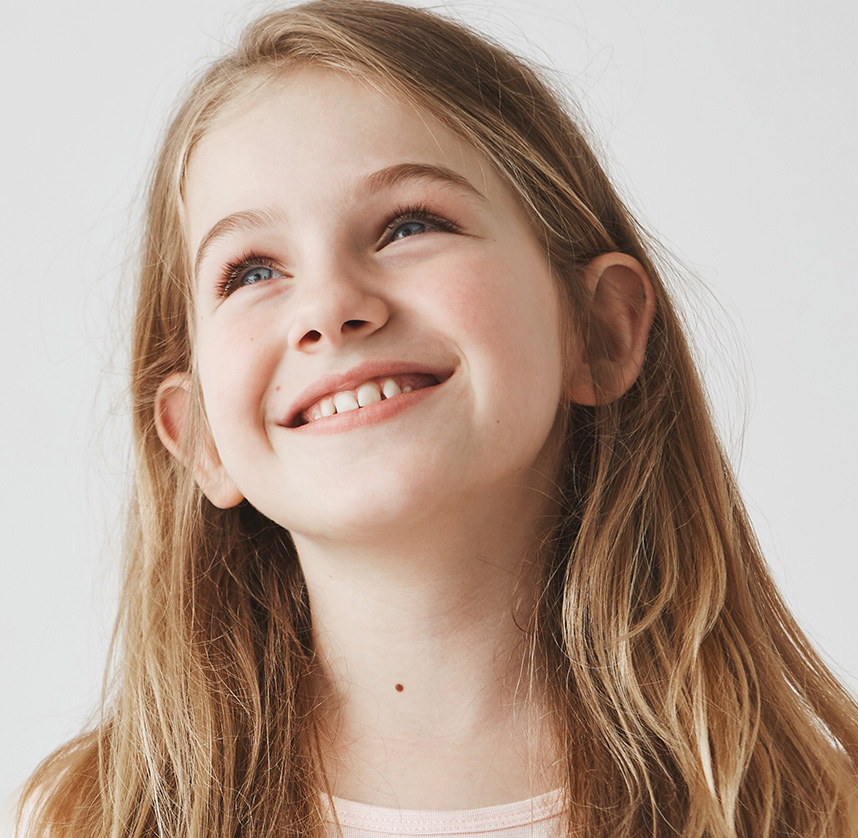

Otoplasty is a surgical procedure that can be performed as early as the age of 6, including adults. The incision (and so the scar) is made behind the ear.
This surgical procedure is most commonly conducted on children between the age of 9 and 12 who have endured teasing since their early school years, around the age of 6, but have now gathered the courage to undergo the surgery.
It is important to mention that in certain instances, when addressing the absence of folding in the upper portion of the ear, EarFold™ procedure may be used as well.
Occasionally,I also treat adults, and I sometimes see the parents of children on whom I have performed the otoplasty surgery.
Otoplasty is a highly rewarding procedure that brings immense joy to the child and significant relief to the parents. Initially, parents may have concerns about the surgical intervention and question its worth. However, their worries are quickly conforted by the sight of their child’s smile.
Otoplasty is a cosmetic surgery procedure covered by Social Security.
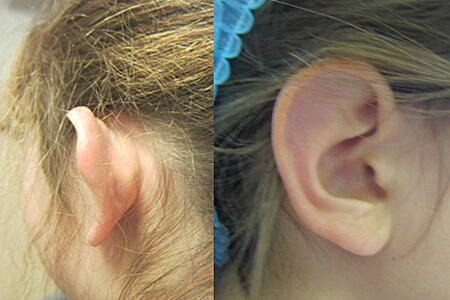
Surgery for prominent ears can be performed as early as the age of 6. A clinical examination helps determine the surgical approach. I explain the scarring, the necessary steps, and provide information about potential complications, including the risk of hypertrophic scarring.
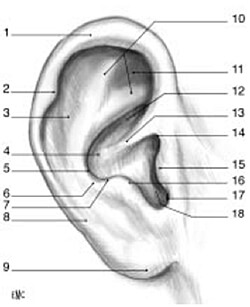
External configuration of the ear
1. Helix; 2. Darwin’s Tubercle; 3. Sca
phoid Fossa; 4. Concha; 5. Antihelix; 6. Root of the Antihelix; 7. Antitragohelicine Fissure; 8. Lobule; 9. Anterior and Posterior Branches of the Antihelix; 10. Navicular Fossa; 11. Cymba of the Concha; 12. Root of the Helix; 13. Preauricular Sulcus; 14. Tragus; 15. Antitragus; 16. Intertragal Notch; 17. External Auditory Meatus.
I was filmed performing the surgical technique for otoplasty and explaining the surgical steps for an episode of “Le Magazine de la Santé” broadcasted on France 5. I often refer patients to this footage during consultations.
The procedure usually lasts about one hour under general anesthesia, which is the most comfortable option for the child. The incision is made behind the ear, and the cartilage is sculpted using a rasp. I use absorbable sutures to avoid leaving any materials in the ears that could cause infection or unsightly scarring. The healing process ensures the desired outcome.
A dressing is then applied around the head to properly hold the ears in place for 3 days. The young patient can usually be discharged the same day or the next morning.
Pain levels vary among patients and can be managed with painkillers. On the third day, the dressing is replaced with a headband. A compression headband should be worn day and night for approximately 15 days, allowing the sutures to dissolve and the healing process to stabilize the outcome. The ears may be slightly swollen and bruised for 8 to 10 days, with the final result being nearly achieved within 15 days. On average, the swelling will completely subside within 4 weeks.
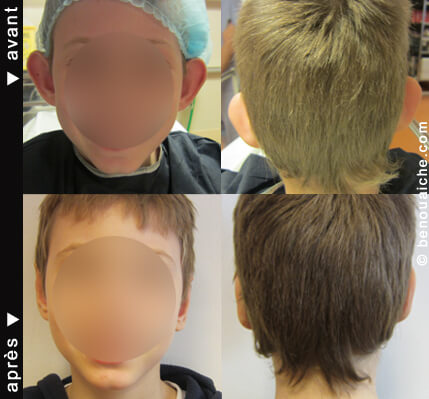
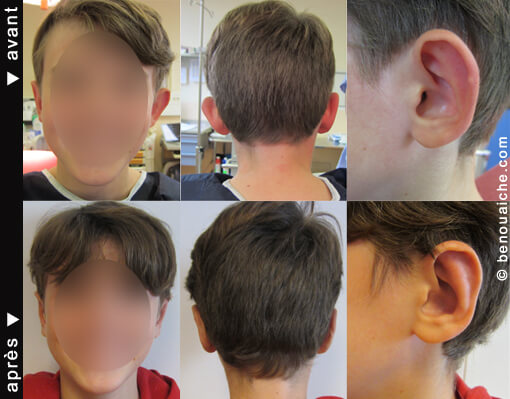
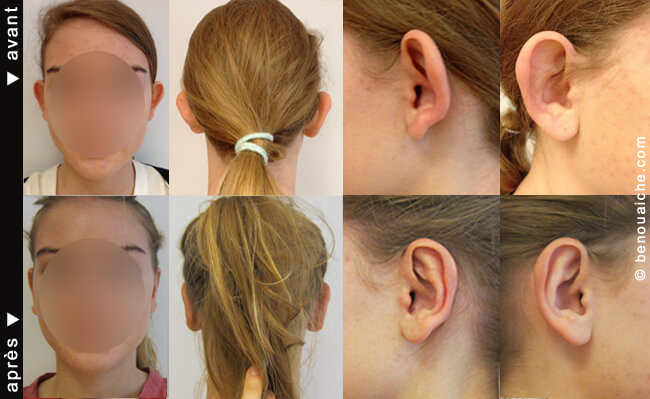
Photos before and after otoplasty

Do you have a question ?
If you would like to receive advice or further information, please do not hesitate to contact me by email
The information provided on this site is not intended to serve as a substitute for medical prescription.
Make an appointment on
Doctolib
INFORMATION ABOUT COOKIES
By browsing this website, you agree to the use of cookies to improve your browsing experience and our services by analyzing website usage.
for more information on our cookies policy and how to configure them, Click here
When you browse our website, you may record or read information on your terminal, depending on your choices.
Do you accept the deposit and reading of cookies to enable us to analyze your browsing habits and measure the audience of our site?
You can also leave me a comment. I will reply as soon as possible.